Blog
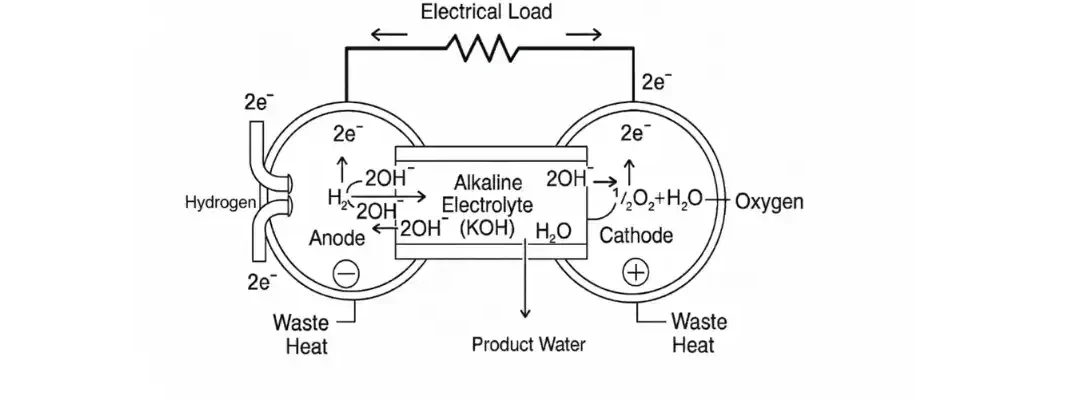
Alkaline Fuel Cells (AFC)
Alkaline Fuel Cells (AFCs) are among the oldest types of fuel cells—and still one of the most efficient for converting hydrogen and oxygen into electricity. They’re compact, lightweight, and ideal for situations where space and energy efficiency matter most. Used by...
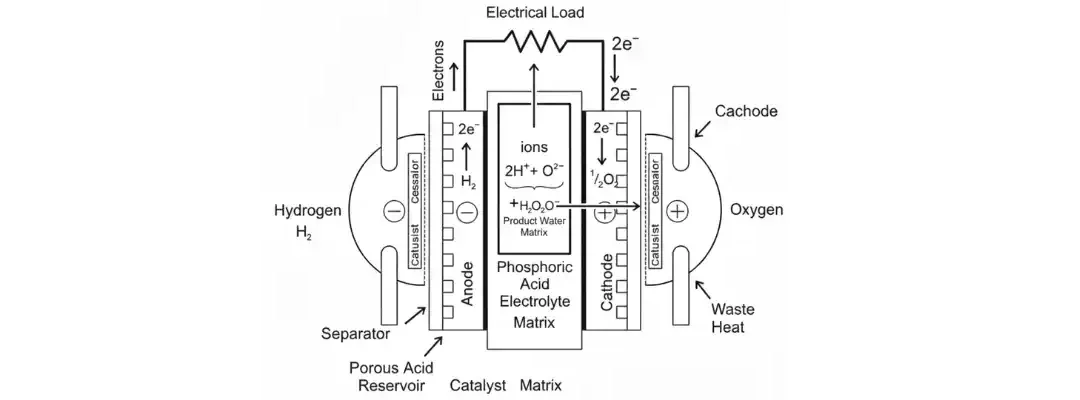
Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells
Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells (PAFCs) are one of the most established types of fuel cells, known for their stable performance, moderate temperature operation, and use in commercial and stationary power systems. PAFCs are well-suited for combined heat and power (CHP) due...
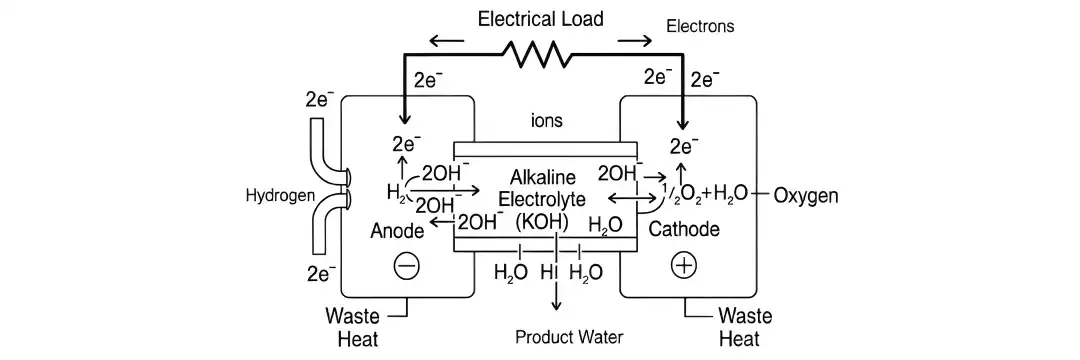
PEM & Direct Methanol Fuel Cells
As the demand for clean, efficient, and compact energy solutions grows, two technologies stand out: Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells and Direct Methanol Fuel Cells (DMFCs). These advanced energy systems are transforming the way we power vehicles, devices, and...
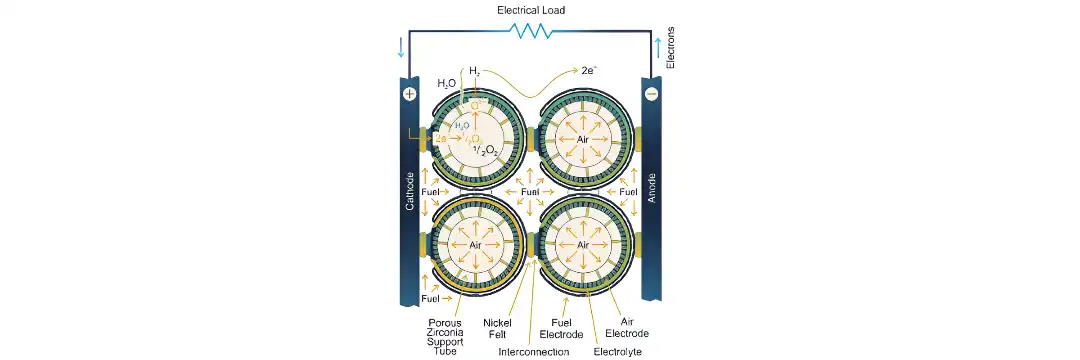
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) are a cutting-edge clean energy solution designed for high-efficiency, long-duration power generation. Unlike other fuel cells that use liquids or polymers, SOFCs utilize a solid ceramic electrolyte and operate at extremely high...
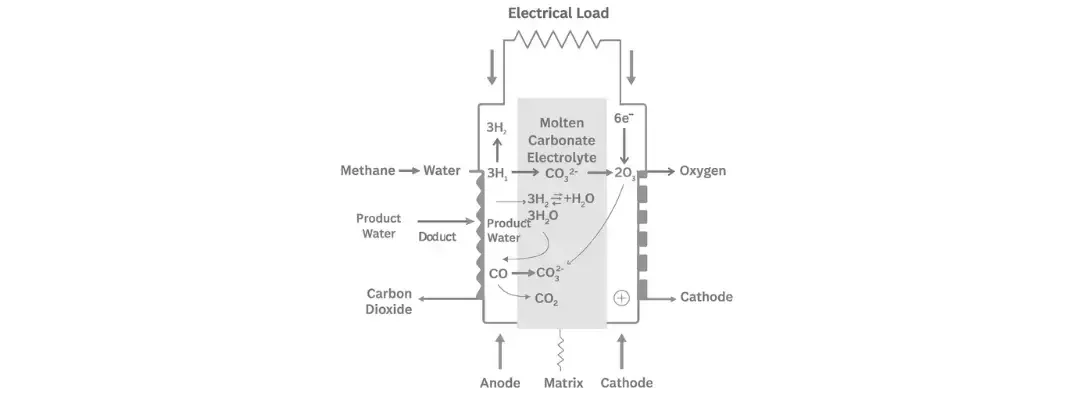
Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells
As the global push for clean and efficient energy systems intensifies, Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFCs) stand out as a compelling solution for high-efficiency stationary power generation, particularly in industrial and utility-scale applications. Unlike...
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology for Material Handling: Advantages & Challenges
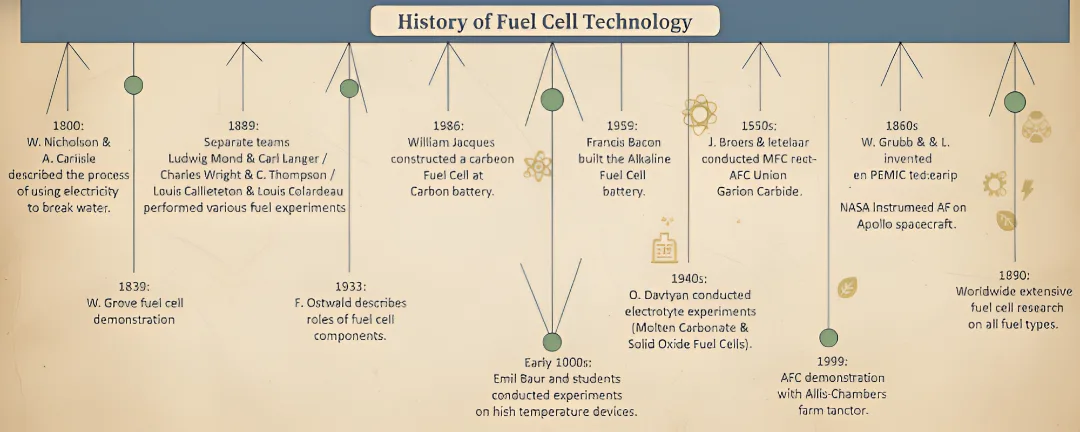
1.1 History of Fuel Cell Technology Fuel cells have fascinated scientists for over 150 years. Their origins can be traced back to 1800 when William Nicholson and Anthony Carlisle discovered how electricity could split water into hydrogen and oxygen. Building on this,...
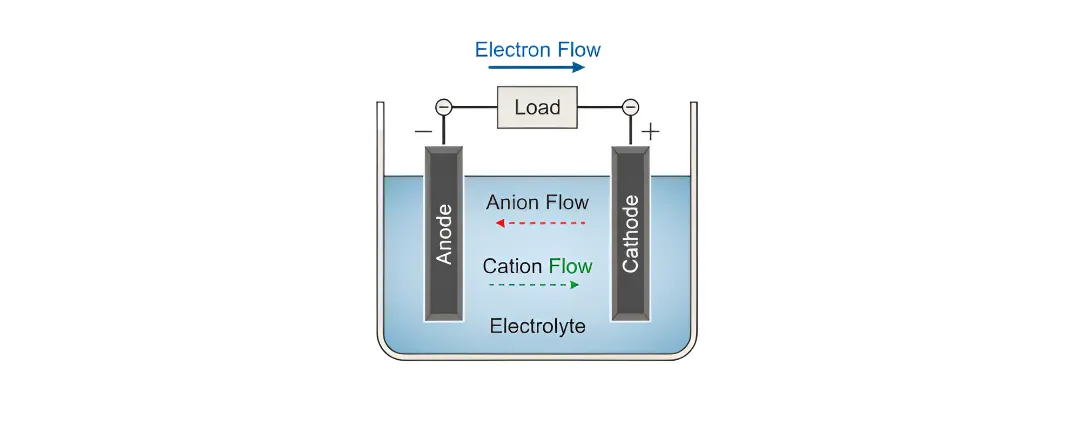
Galvanic Cells: The Electrochemical Engines Powering Modern Energy Solutions
Galvanic cells are at the heart of technologies that power everything from portable electronics to electric vehicles. These electrochemical cells transform chemical energy into electrical energy through spontaneous redox reactions. In this blog, we explore how...
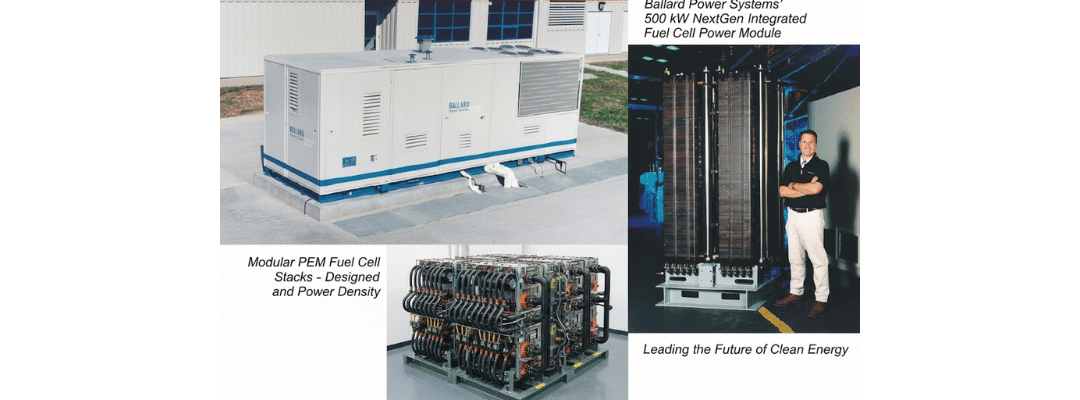
Fuel Cell Applications: Power Plants to Hydrogen Cars
Fuel cells, thanks to their modular nature, span a broad spectrum of use‑cases—from large stationary power plants down to portable power packs. Stationary Power Plants Fuel cell systems are increasingly employed for stationary electricity generation, backup power and...
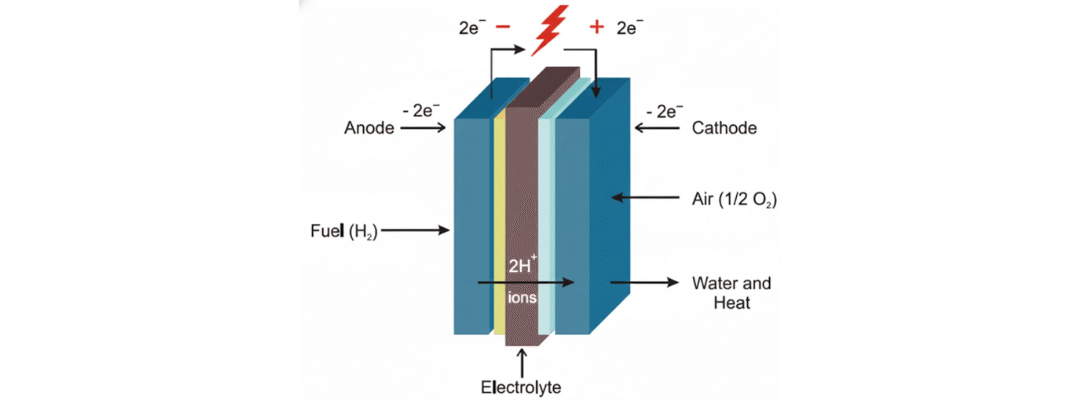
Types of Fuel Cells: High vs. Low Temperature Technologies Explained
Fuel cells are an advanced clean energy technology, capable of powering everything from vehicles to industrial plants. But not all fuel cells are created equal. The type of electrolyte used inside a fuel cell determines how it operates, what fuels it can use, what...
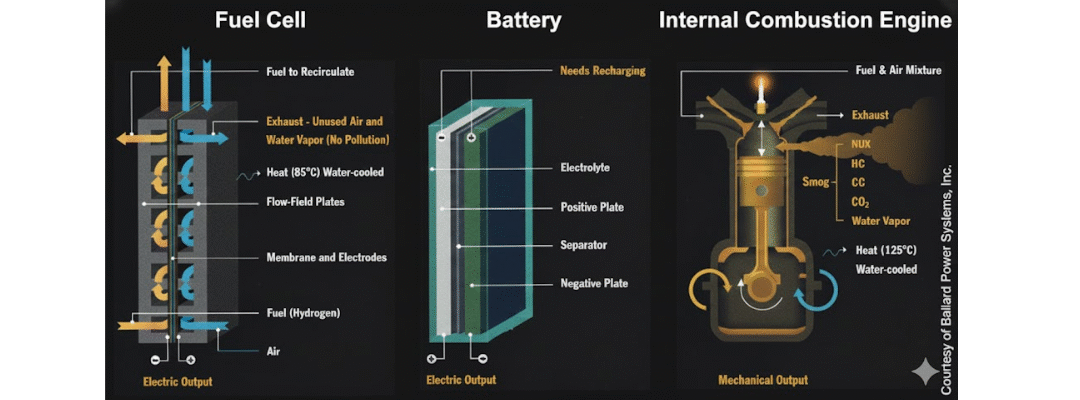
Fuel Cells and Internal Combustion Engines: Evaluating Modern Powertrain Technologies
As the world transitions to cleaner energy solutions, understanding how fuel cells compare to traditional internal combustion engines (ICEs) is essential. While both systems can run on hydrogen-based fuels, they differ fundamentally in how they generate power and...
